What Is Leverage in Trading and How Does it Work?
)
For many, trading with leverage is both enticing and intimidating. This tool promises enhanced gains but also carries the weight of potential disaster if not handled with care. In the trading world, leverage isn't just a financial tool, it's more about psychology. How you handle it can decide if you're headed towards potential profits or significant losses.
In this article, we'll find out the true nature of leverage trading, revealing why it can be your best ally or your worst enemy. Whether you're trading stocks, forex, and other leveraged products, understanding this instrument is crucial to mastering the markets.
Table of Contents
KEY TAKEAWAYS
WHAT IS LEVERAGE TRADING?
HOW DOES LEVERAGE WORK?
LEVERAGE TRADING: PRACTICAL EXAMPLES
SHORT POSITION VS. LONG POSITION
WHAT IS MARGIN TRADING?
LEVERAGE IN FOREX TRADING
DIFFERENT TYPES OF LEVERAGED PRODUCTS
BENEFITS AND RISKS OF USING LEVERAGE
RISKS OF USING LEVERAGE
RISK OF EXCESSIVE REAL LEVERAGE IN FOREX TRADING
LEVERAGE AND RISK MANAGEMENT
HOW DOES FOREX MARGIN COMPARE TO STOCK TRADING?
ARE FOREX MARKETS VOLATILE?
HOW MUCH LEVERAGE SHOULD I USE?
CONCLUSION
FAQS
Key Takeaways
- Leverage is a financial tool that implies borrowing money from a broker to open larger positions and gain greater exposure to the market.
- Trading with leverage comes with the potential for higher profits and for amplified losses.
- Forex market offers higher leveraged trading ratios, such as 100:1, 200:1, and more.
- Trading with leverage requires robust risk management and trading experience.
What is Leverage Trading?
Leverage, also known as margin trading, is a financial strategy that allows traders to open larger positions than they could with their own capital alone. By borrowing funds from a broker, traders can increase their market exposure while only committing a fraction of the total trade value upfront. This fraction is called the margin, and it represents the portion of the position size that the trader must deposit.
The leverage ratio—such as 10:1 or 50:1—indicates how much larger the position can be compared to the capital invested. For example, with a 10:1 leverage ratio, a trader can control a $10,000 position with just $1,000 of their own money. While this amplifies potential profits from favorable price movements, it equally magnifies the risk of losses, making risk management essential.
Leverage trading is commonly used by those speculating on short-term price changes in forex, stocks. However, because most of the capital comes from the broker, poor decisions can quickly lead to significant losses. Therefore, traders must understand the mechanics of leverage, use it cautiously, and implement solid risk controls.
How Does Leverage Work?
Leverage allows traders to increase their buying power by using a small deposit (called margin) to gain larger exposure to an underlying asset. The rest of the position’s value is borrowed from the broker, enabling control of a much larger trade than their capital would normally allow.
This mechanism is defined by the leverage ratio—such as 5:1, 10:1, or 50:1—which shows how much more than the margin a trader can control. For example, with 10:1 leverage, a $1,000 margin allows access to a $10,000 position.
Here’s how leverage works in practice:
- Deposit (Margin): The trader puts down a small portion of the total trade value.
- Leverage Ratio: Determines how much buying power the margin provides.
- Borrowing from Broker: The broker supplies the remaining capital.
- Exposure: The trader gains access to the full value of the leveraged position.
- Profit and Loss Calculation: Based on the entire position size, not just the margin.
Example:
A trader wants to buy $50,000 worth of EUR/USD. With 20:1 leverage, they only need to deposit $2,500 in margin. If the currency pair moves 1% in their favor, the profit is $500—20% of their initial margin. But if it moves 1% against them, they also lose $500, highlighting the need for careful risk control.
Is Leverage Trading Profitable?
Leverage trading offers the potential for significant profits, particularly by magnifying gains from small price movements. This is one reason why it has become increasingly popular across forex, stock. Traders can capitalize on minor shifts in price with relatively small amounts of capital, making leverage an appealing tool for those seeking to maximize returns.
However, while the profit potential is high, so is the risk. Because profits and losses are calculated on the full position size—not just the margin—traders can lose much more than their initial deposit if the market turns against them. In extreme cases, a few unfavorable moves in a volatile market can wipe out an entire account balance.
Therefore, leverage trading is not inherently profitable or unprofitable—it depends on how it's used. Successful leveraged trading requires:
- A solid understanding of the markets
- Strict risk management practices
- The ability to control emotions and avoid overleveraging
- Experience in managing trades during market volatility
In short, while leverage can amplify gains, it equally amplifies losses, making it essential for traders to approach it with caution, skill, and proper preparation.
Leverage Trading: Practical Examples
Understanding how leverage trading works is best done through clear, practical examples. Let’s compare leveraged and non-leveraged scenarios when buying shares, highlighting the impact on profit, loss, and overall risk.
Example 1: Buying Shares Without Leverage
A trader wants to buy 100 shares of a stock priced at $50 each.
- Investment required: $5,000
- No leverage used
If the stock price rises to $55:
- New value of position: $5,500
- Profit: $500
- Return on investment: 10%
If the stock drops to $45:
- New value of position: $4,500
- Loss: $500
- Return on investment: –10%
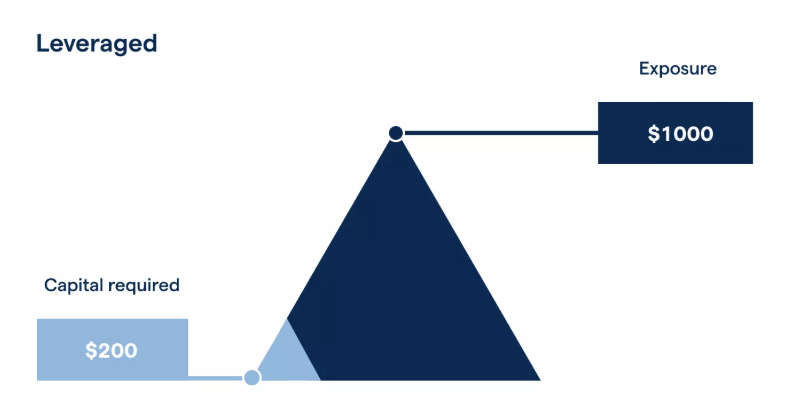
Example 2: Buying Shares With 5:1 Leverage
Now the trader uses a leverage ratio of 5:1 to open the same $5,000 position.
- Margin amount (from trader): $1,000
- Borrowed funds (from broker): $4,000
If the stock rises to $55:
- Position value: $5,500
- Profit: $500
- Return on trader's capital: 50% ($500 gain on $1,000 margin)
If the stock falls to $45:
- Position value: $4,500
- Loss: $500
- Return on trader's capital: –50%
If the price drops further to $40, the trader’s entire margin amount could be lost, and their trading account may even owe additional funds, depending on the broker’s terms.
These examples show how leverage increases both potential returns and portfolio impact. While a long position with leverage can yield higher profits, it also exposes the trader to amplified losses. This underlines the importance of managing risk and using leverage cautiously.
How Unleveraged Trades Work
Unleveraged trading involves purchasing an asset by paying its full value upfront, without borrowing funds from a broker. This means the trader must commit the entire capital outlay required to open the position. For example, buying 100 shares at $50 each in an unleveraged trade would require a $5,000 investment from the trader’s own funds.
While this approach demands more initial capital, it offers a key advantage: limited risk. The maximum potential loss in an unleveraged trade is capped at the amount invested. If the stock’s price drops to zero, the trader loses $5,000—no more. There's no risk of owing additional funds, unlike in leveraged positions where losses can exceed the initial margin.
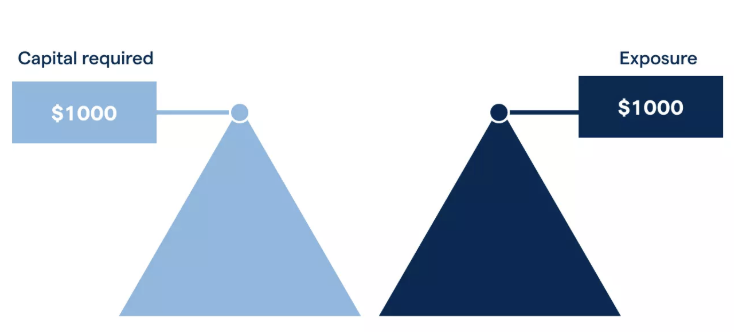
This makes unleveraged positions particularly suitable for risk-conscious investors, as they provide more control and eliminate the danger of margin calls or account wipeouts. The risk profile of unleveraged trading is fundamentally different from leveraged trading:
- Losses are limited to the capital invested
- There’s no borrowing involved
- No exposure to amplified price movements
Although unleveraged trading may result in slower gains, it offers greater financial stability and reduces emotional pressure, making it a prudent choice for many traders.
Short Position vs. Long Position
Long position (going long) means buying an underlying asset, expecting that its price will go up, so you can gain profit by selling it afterward at a higher price. A short position (going short), on the contrary, implies selling an underlying asset you don’t own, expecting to buy it in the future at a lower price.
What is Margin Trading?
Margin trading allows investors to borrow money from a broker to purchase more securities than they could with their own capital. This is done through a margin account, where the broker lends funds based on a percentage of the total investment, known as the margin requirement. The borrowed amount is subject to an interest rate, which the trader must repay alongside the principal.
However, it’s crucial to remember about the risks. If the total value of the position falls below the specified level the trader may receive so called margin call. It’s a requirement to add additional funds to the account or liquidate financial instruments in order to meet the necessary margin. Not meeting a margin call could cause the broker to sell off the trader's investments and result in high losses.
Leverage in Forex Trading
Leveraged trading is a crucial feature in the forex market. It allows traders to control large positions with a relatively small initial outlay. In the foreign exchange, brokers often offer higher leverage ratios, sometimes as much as 100:1 or even 500:1. Consequently, with just $10, a trader could control a position worth $1000 or more.
Yet, don’t forget that forex is a highly liquid and volatile market. This means that even small market moves in combination with high leverage can result in significant losses. This market requires strict discipline and a clear understanding of its risks.
Different Types of Leveraged Products
Most leveraged trading is conducted through derivative products, which allow traders to speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset. One of the most common derivatives used is the CFD (contract for difference). CFDs are offered by many online brokers and enable traders to profit from both rising and falling markets by opening long or short positions.
Other forms of leveraged trading include:
- Spot trading: Immediate execution of buy/sell orders, often available with leverage in forex.
- Futures contracts: Agreements to buy or sell an asset at a set price on a future date, commonly used in commodities and indices.
- Options: Derivatives that give the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset, offering leveraged exposure with defined risk.
Leveraged trading is available across various markets, including:
- Shares: Trade price movements of individual stocks without owning them.
- Forex: Highly liquid and commonly leveraged market for currency pairs.
- Indices: Gain exposure to entire markets like the S&P 500 or FTSE 100.
- Commodities: Speculate on resources like oil, gold, or agricultural goods.
- ETFs: Trade diversified asset baskets with leverage, enhancing returns and risks.
Each market and product type offers unique benefits and risks, making it essential for traders to choose instruments that align with their strategy and risk tolerance.
Benefits and Risks of Using Leverage
Leverage can significantly enhance a trader’s profit potential, especially in markets with small price movements. By using a small amount of capital to control a larger position, traders can access opportunities that might otherwise be out of reach. Leverage also increases market participation and portfolio diversification by freeing up capital for other trades.
However, leverage also amplifies risk. Losses are calculated on the full position size—not just the margin—meaning a small adverse move can quickly lead to significant losses. In extreme cases, a trader’s entire account can be wiped out, especially in volatile markets. Effective risk management, such as stop-loss orders and appropriate position sizing, is essential when trading with leverage.
Pros:
- Amplifies potential profits
- Requires lower initial capital
- Increases market access and flexibility
- Allows for greater diversification
Cons:
- Amplifies potential losses
- Risk of margin calls or account liquidation
- Requires careful monitoring and discipline
- Not suitable for inexperienced traders
Used wisely, leverage can be a powerful tool—but only with a clear understanding of the risks and responsibilities involved.
Risks of Using Leverage
- Increased losses. Leverage works both ways: not only does it amplify potential profits but it also leads to more significant losses if the market moves against trader’s expectations.
- Margin call risk. The broker may ask the trader to deposit more money if the market goes against him to cover the margin requirement. Otherwise, the broker can sell the trader’s positions to cover the loss.
- High overall risk. Leverage is a complex instrument that needs much experience to limit its trading risks and avoid high potential losses.
Risk of Excessive Real Leverage in Forex Trading
Excessive use of maximum leverage in forex trading can lead to substantial losses. For example, if a trader uses 100:1 leverage with $1,000, they control a $100,000 position. A mere 1% adverse market movement in the forex pair would result in a $1,000 loss, wiping out the initial investment. As we can see, such high leverage ratios can quickly turn a promising trade into a significant financial setback.
Leverage And Risk Management
Effective risk management is critical when trading with leverage, as amplified exposure increases both profit potential and the risk of substantial losses. Without solid precautions, even minor price movements can severely impact a trader’s balance. Fortunately, brokers and leverage trading platforms offer a variety of tools to help mitigate these risks.
Key protective tools include:
- Stop-loss orders – Automatically close a position at a pre-set level to limit losses.
- Guaranteed stops – Ensure closure at the exact price level, even in volatile conditions.
- Negative balance protection – Prevents the trader’s account from falling below zero, ensuring losses never exceed deposits.
To further reduce risk and improve trading outcomes, here are eight essential strategies:
-
Use Conservative Leverage Ratios
Start with low leverage (e.g., 2:1 or 5:1) to minimize exposure and reduce the chance of margin calls.
-
Set Stop-Loss Orders for Every Trade
Define maximum acceptable loss in advance to protect your capital on each position.
-
Regularly Monitor Open Positions
Active oversight allows for timely responses to market shifts and prevents losses from spiraling.
-
Control Emotions During Trades
Avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed; stick to your strategy and remain disciplined.
-
Invest in Proper Education
Study financial markets, technical analysis, and trading psychology before trading with real money.
-
Adjust Position Sizes in Volatile Markets
Reduce trade sizes when volatility increases to manage unpredictable swings.
-
Develop a Clear Exit Strategy
Know in advance when and why to exit a trade—whether in profit or loss.
-
Practice with a Demo Account First
Use a simulated environment to test strategies and gain experience without risking real money.
Combined with maintaining sufficient funds in your trading account, these risk management practices greatly improve the odds of long-term success in leveraged trading.
How Does Forex Margin Compare to Stock Trading?
Forex margin usually offers much higher leverage than stock trading. In the stock market, leverage is more limited, capped around 2:1. In forex, in turn, it can reach 100:1, 200:1, and even more. The maximum leverage in forex means quicker gains, but as mentioned above, it also increases the potential for rapid losses.
Are Forex Markets Volatile?
Forex is known for its high volatility. Currency prices can fluctuate quite rapidly due to various factors like economic data releases, political events, central bank policies, etc. As we already know, higher market volatility implies more trading opportunities but also higher trading risks.
How Much Leverage Should I Use?
The right amount of leverage depends on your personal circumstances, including risk tolerance, trading experience, financial goals, and how much time you can dedicate to the markets. Leverage trading isn’t for everyone—it requires discipline, a clear strategy, and access to sufficient capital.
Beginners are typically advised to start with low leverage, such as 5:1, to manage risk while building experience. More seasoned traders may use higher ratios, but even then, caution is essential.
Leverage should align with your investment goals and emotional control. If you can’t afford large losses or closely monitor your trades, using high leverage may be inappropriate. Maintaining a diversified portfolio also helps reduce risk.
Choosing the right platform is just as important. Opt for solutions like J2T, known for strong risk management tools and customizable leverage features, allowing you to tailor your setup to your strategy.
In short, only use as much leverage as you can responsibly manage—balancing potential reward with the real possibility of loss.
Conclusion
Trading with leverage can be helpful for many traders. However, remember while the allure of larger profits is strong, it's crucial to approach this tool with caution. Use stop-loss orders, price alerts, and choose the right leverage ratio. Last but not least, keep educating yourself to mitigate potential risks and get better results from your strategies.
FAQs
What does 1 to 500 leverage mean?
1:500 leverage means you can control a position 500 times larger than your deposit. With $100, you can open trades worth up to $50,000, increasing both profit and loss potential significantly.
How does leverage trading work?
Leverage trading uses borrowed funds from a broker to open larger positions. The trader deposits margin, and the broker provides the rest. Profits and losses are calculated on the full position size, not just the margin.
What leverage is good for $100?
For a $100 account, leverage between 5:1 and 20:1 allows manageable exposure with reduced risk. Higher leverage increases volatility and can quickly deplete small balances with minor market movements.
What is a good leverage for trading?
Good leverage depends on experience and risk appetite. Conservative ratios like 5:1 or 10:1 offer balanced exposure and risk control. Excessive leverage increases potential losses and is better suited to advanced traders.
What is the best leverage for $5?
With only $5, leverage should be minimal—no more than 10:1. The small account size makes it highly susceptible to quick losses, even with small price changes. Conservative risk management is essential.
Is 20X leverage too much?
20X leverage can be high for most traders. It amplifies small price movements and increases the chance of margin calls. Without strict risk control, such leverage can quickly lead to full account loss.
What is a good leverage for a beginner?
Beginners should start with low leverage, ideally between 2:1 and 5:1. This reduces the chance of rapid losses and allows time to learn market behavior while managing positions safely.
Is leverage trading illegal?
Leverage trading is legal in most jurisdictions but regulated differently. Brokers must comply with local rules, which often limit maximum leverage based on market type and trader classification.
Do professional traders use leverage?
Professional traders frequently use leverage but combine it with strict risk management. They use leverage strategically to enhance returns while carefully controlling exposure and potential downside.